What is the Gstr 2?










GSTR-2 is a monthly return that summarizes the details of inward purchases of taxable goods and/or services.
GSTR-2 is a monthly return that summarizes the details of inward purchases of taxable goods and/or services. In this article, we discuss the following topics:
Contents
- What is GSTR-2?
- Why is GSTR-2 important?
- What is buyer-seller reconciliation?
- When is GSTR-2 due?
- What happens if GSTR-2 is not filed?
- What happens if GSTR-2 is filed late?
- Who should file GSTR-2?
- How to revise GSTR 2?
- What is GSTR-2A?
- How to file GSTR 2 on ClearTax GST software?
- Details to be provided in GSTR-2
Advanced GST Reconciliation Tool – ClearTax GST
1. What is GSTR-2?
Every registered taxable person is required to give details of Inward Supply, i.e., purchases for a tax period in GSTR-2.
2. Why is GSTR-2 important?
GSTR-2 contains details of all the purchases transactions of a registered dealer for a month. It will also include purchases on which reverse charge applies.
The GSTR-2 filed by a registered dealer is used by the government to check with the sellers’ GSTR-1for buyer-seller reconciliation.
3. What is buyer-seller reconciliation?
Buyer-seller reconciliation or invoice matching or is a process of matching taxable sales by the seller with the taxable purchases of the buyer.
It is vital because ITC on purchases will only be available if the details of purchases filed in GSTR-2 return of buyer matches with the details of sales filed in GSTR-1 of the seller.
For example, Ajay buys 100 pens worth Rs. 500 from Vijay Stationery. Vijay Stationery must show Rs. 500 sales in his GSTR-1. Ajay must show the same Rs. 500 purchase in GSTR-2 to claim ITC. Unless the amounts match, Ajay will not be able to claim ITC.
Note: Most of the headings under GSTR-2 are auto-populated from counter-party GST return so it will involve minimal time.
4. When is GSTR 2 due date?
As per the Act: GSTR-2 due date for Filing GSTR-2 is 15th of next month.
There is a 5-day gap between GSTR-1 & GSTR-2 filing to correct any errors and discrepancies.
For business’ with turnover less than 1.5 crores, quarterly returns are applicable whose due dates will be announced later.
Latest Update for July 2017:
GST Due date for GSTR-2 for July has been extended to 30th Nov
As per 22nd GST Council meeting of 6th October 2017
- Businesses with annual turnover up to 1.5 crores will submit quarterly returns. Taxes will be paid quarterly.
- Due dates of Aug & Sep will be declared later.
- Switch over to quarterly will happen from Oct-Dec 2017 cycle
(More details will be announced by the Govt.)
5. What happens if GSTR-2 is not filed?
If GSTR-2 return is not filed then the next return GSTR-3 cannot be filed. Hence, late filing of GST return will have a cascading effect leading to heavy fines and penalty.
6. What happens if GSTR-2 is filed late?
If you delay in filing, you will be liable to pay interest and a late fee.
Interest is 18% per annum. It has to be calculated by the taxpayer on the amount of outstanding tax to be paid. The time period will be from the next day of filing (16th of the month) to the date of payment.
The late fee is Rs. 100 per day per Act. So it is 100 under CGST & 100 under SGST. Total will be Rs. 200/day. The maximum is Rs. 5,000.There is no late fee on IGST.
7. Who should file GSTR-2?
Every registered person is required to file GSTR-2 irrespective of whether there are any transactions during the month or not.
However, these registered persons do not have to file GSTR 2 –
- Input Service Distributors
- Composition Dealers
- Non-resident taxable person
- Persons liable to collect TCS
- Persons liable to deduct TDS
- Suppliers of online information and database access or retrieval services (OIDAR), who have to pay tax themselves (as per Section 14 of the IGST Act)
8. How to revise GSTR 2?
GSTR 2 once filed cannot be revised. Any mistake made in the return can be revised in the next month’s return. It means that if a mistake is made in September GSTR 2, rectification for the same can be made in October’s GSTR 2.
9. What is GSTR-2A?
When a seller files his GSTR-1, the information is captured in GSTR-2A. GSTR-2A is a purchase-related tax return that is automatically generated for each business by the GST portal.
It takes information from the seller’s GSTR-1. You are required to verify (and amend) this return before filing in on GST Portal.
10. How to file GSTR 2 on ClearTax GST software?
- Make sure all your purchase invoices are in the software – by using Excel Import or importing through other software.
- While uploading purchase bills, you can select bills on which reverse charge will apply.
- Our software will read your day’s invoices. If you cross the threshold of Rs. 5,000, it shows an alert message saying that your aggregate purchases from URDs have exceeded Rs. 5,000. “Please verify: There are one or more unregistered purchase invoices under reverse charge without any tax (no or 0 tax) in your data. As per GST rules you should add appropriate tax amount against such invoices before filing.”
- Our software will identify invoices which do not have any GSTIN and can be subject to RCM
- Our software will track invoices and remember their treatment. If an invoice from same GSTIN is already marked as under reverse charge, system will alert the user that a similar invoice from same GSTIN had already marked under reverse charge and hence the new invoice may also be under reverse charge.
- Download your seller’s return from GST Portal through our software. The software will automatically highlight any mismatches between you purchases and your vendor’s sales.
- Finally, validate data and upload to the government GST portal.
11. Details to be provided in GSTR-2
There are 13 headings in GSTR-2 format prescribed by the government.
We have explained each heading along with the details required to be reported under GSTR-2.
1.GSTIN – Each taxpayer will be allotted a state-wise PAN-based 15-digit Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number (GSTIN). A format of proposed GSTIN has been shown in the image below. GSTIN of the taxpayer will be auto-populated at the time of return filing.

2.Name of the Taxpayer – Name of the taxpayer including legal and trade name (will be auto-populated)
Month, Year – Mention the relevant month and year for which GSTR-2 is being filed.

3.Inward Supplies from Registered Taxable Person
Most of the purchases from a registered person will be auto-populated here from GSTR-1 filed by the seller. It will have all details of type, rate and amount of GST, whether ITC is eligible, amount of ITC.
However, it will not contain purchases under reverse charge

Certain transactions may not be auto-populated because-
- Seller did not file GSTR-1
- Seller filed GSTR-1 but he missed the transaction
In either case, the buyer can manually add these transactions. The seller will get a notification to accept this addition/modification in his GSTR-1A return.
If the supply is received in more than one lots, the invoice must be reported in the return of the month in which the last lot is received and recorded in books of accounts.
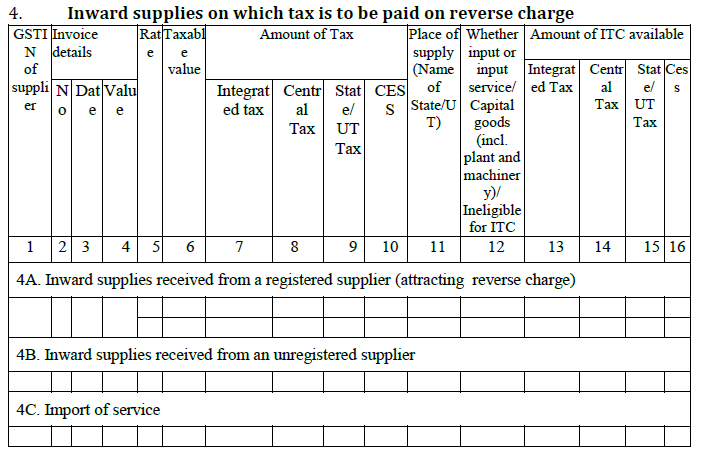
- Inward supplies on which tax is to be paid on reverse charge
Certain goods and services attract reverse charge, i.e., the buyer is liable to pay GST. A registered dealer purchasing more than Rs. 5,000 per day from an unregistered dealer is liable to pay reverse charge.
All purchases on which reverse charge applies, will be reported in this part.
4A. Under this head, all purchases on which reverse charge specifically applies by law must be mentioned. For example, purchasing cashew nuts from an agriculturist.
4B. This head will list the purchases from unregistered dealer which exceed Rs. 5,000 per day from an unregistered dealer
4C. Under this head, reverse charge GST paid on import of service will be reported.

- Inputs/Capital goods received from Overseas or from SEZ units on a Bill of Entry
Any kind of import of inputs (items used to manufacture finished goods) or capital goods received against a Bill of Entry must be reported under this head. Goods received from SEZ are also reported here.
- 5A. Imports: Any kind of import of inputs (items used to manufacture finished goods) or capital goods received against a Bill of Entry will be reported here. Details of bills of entry, along with 6-digit port codes and 7-digit bill numbers must be mentioned.
- 5B. Received from SEZ: Inputs or capital goods received from sellers in a SEZ will be reported here.

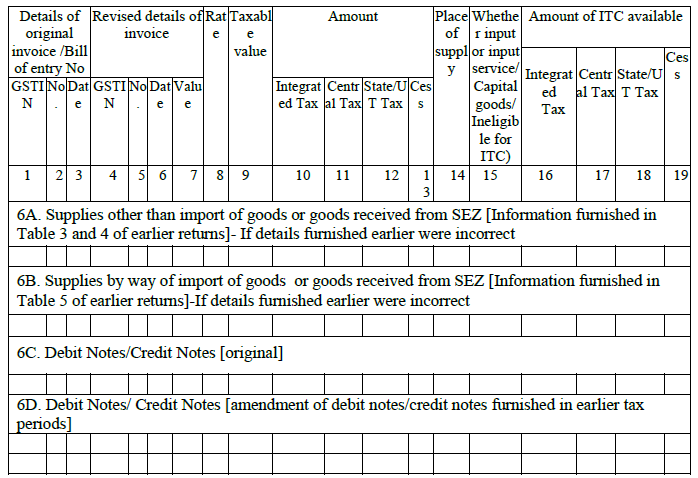
- Amendments to details of inward supplies furnished in returns for earlier tax periods in Tables 3, 4 and 5 [including debit notes/credit notes issued and their subsequent amendments]
A taxpayer cannot revise any GST return once it is filed. Revision is possible only in the next month’s return under this heading. The taxpayer can amend any detail of purchases of goods/services in earlier months. This information can be filled manually. Subsequently, the seller will also get a notification regarding this modification. The seller needs to accept this change in his GSTR-1A return.
6A. This head will contain all revisions of input goods/services (except imports)
6B. Any change in amount/tax calculated on imported goods and goods from SEZ can be made under this heading. Here, the taxpayer must mention the changes made in the bill of Entry / Import Report.
6C. The taxpayer must report all debit and credit notes issued with respect to purchases. Any debit/credit note issued under reverse charge mechanism will get auto-populated here from counter-party GSTR-1 and other applicable returns (eg. GSTR-5 filed by NR).
6D. Any changes in debit /credit note of previous months will be reported under this heading.

- Supplies received from composition taxable person and other exempt/Nil rated/Non-GST supplies received
This head will include purchases from composition dealer and other exempt/nil/non-GST supplies.
Non-GST supplies include items like petrol, diesel which are not covered under GST. Also, both inter-state and intra-state supplies need to be reported here.

- ISD credit received
Details of the input tax credit received from a registered Input Service Distributor (ISD) (usually a head office which has transferred its ITC to all its branches). This data will be auto-populated from GSTR-6 filed by ISD.

- TDS and TCS Credit received
TDS Credit Received – This section will only be applicable in case you engage in specified contracts with specified persons (usually government bodies). The receiver (government) will deduct a certain percentage of transaction value as Tax Deduction at Source. All information will get auto-populated here from GSTR-7 filed by the deductor.
TCS Credit Received – This heading is applicable for only online sellers registered with e-commerce operator. E-commerce operator is required to collect tax at source at the time of making payment to such sellers. This information will again be auto-populated from GSTR-8 of e-commerce operator.
Please read our Impact Analysis on E-commerce marketplace sellers for more information.

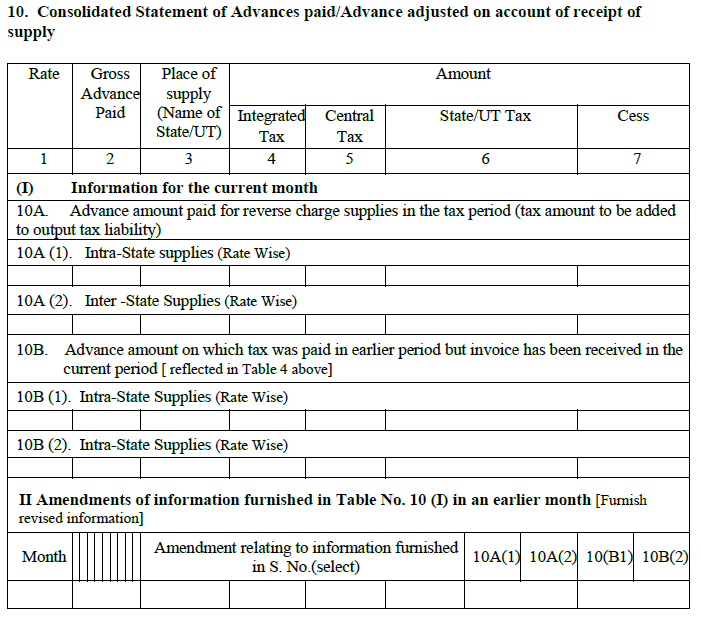
- Consolidated Statement of Advances paid/Advance adjusted on account of receipt of supply
Any advance payment made during the month will appear here. If you paid advance tax on goods or services received during an earlier tax period, but only received the invoices this month, declare the details here.
Advance receipts issued under reverse charge are also covered here.
Normally the seller issues an advance receipt when he receives any advance payment. In case of purchases attracting reverse charge, the buyer must issue the advance receipt if he pays in advance.
Part I –
- This part will cover the advance amount paid for reverse charge supplies in the current month.
- It will also include the advances paid in earlier months against which invoices have been received in current month.
- The purchases will be broken up into inter-state and intra-state.
Part II will contain changes to above part I in relation to an earlier month.

- Input Tax Credit Reversal / Reclaim
ITC can be availed only on goods and services for business purposes. If they are used for non-business (personal) purposes, or for making exempt supplies ITC cannot be claimed.
In this heading, the taxpayer must to fill in details of ITC that cannot be claimed during the month due to various ITC rules.
11A. This head will cover all input tax reversal for the current month. It will also include ITC reversal on account of exempt and personal supplies.
a. Amount in terms of rule 37(2)– ITC will be reversed for invoices which were not paid within 180 days of issue.
b. Amount in terms of rule 39(1)(j)(ii)– This is for ISDs. If a credit note was issued by the seller to the HO then the ITC subsequently reduced will be reversed.
c. Amount in terms of rule 42(1)(m)– This is for businesses which use inputs for both business and non-business (personal) purpose. ITC used in the portion of input goods/services used for personal purpose must be reversed proportionately.
d. Amount in terms of rule 43(1)(h)– This is similar to above except that it concerns capital goods.
e. Amount in terms of rule 42 (2)(a)– This is calculated after the annual return is furnished. If total ITC on inputs of exempted/non-business purpose is more than the ITC actually reversed during the year then the difference amount will be added to output liability. Interest will be applicable.
f. Amount in terms of rule 42(2)(b)– This is is the opposite of the above. If total ITC on inputs of exempted/non-business purpose is less than the ITC actually reversed during the year then the difference amount can be reclaimed as ITC.
Read our article on Reversal of Input Tax Credit to understand this in details.
11B. The taxpayer can manually amend any details of ITC under 11A of earlier months. He will select the appropriate information from a drop-down menu.

- Addition and reduction of amount of output tax for mismatch and other reasons
This section will capture any additional tax liability that can arise due to the corrections made to the GSTR-3 of the previous month.
a) ITC claimed on mismatched/duplication of invoices/debit notes: In case mismatch of invoices, there may be double claiming of ITC. The excess ITC claimed from duplicate purchase invoices will be reversed and added to the tax liability.
b) Tax liability on mismatched credit notes: Incorrect credit notes issued by the taxpayer will also result in incorrect ITC. Extra ITC claimed due to mismatch will now be added to your tax liability.
c) Reclaim on account of rectification of mismatched invoices/debit notes: This is the opposite of point (a). In this case, the mismatch has led to claiming lower ITC. You are entitled to more ITC and so the additional amount will be reduced from the output tax liability.
d) Reclaim on account of rectification of mismatched credit note (Reduce): This is opposite to (b), i.e., lower ITC has been claimed and will work in the same way as (c).
e) Negative tax liability from previous tax periods:This is due to excess tax paid during the previous months and will be reduced from output tax liability of this month.
f) Tax paid on advance in earlier tax periods and adjusted with tax on supplies made in current tax period (Reduce): This refers to tax paid along with advance payments in earlier months for supplies received during this month.

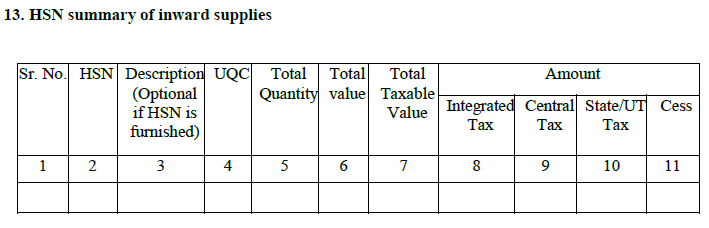
13.HSN summary of inward supplies
This section requires a registered dealer to provide HSN wise summary of goods purchased. It willbe entered by the taxpayer.

Finally, sign off with a declaration that all information has been supplied and is correct.

No comments:
Post a Comment